分析
Previewing The Bernanke Review: A Major Shift In How The BoE Operates

Helpfully, the BoE have published the ‘Terms of Reference’ to which Bernanke’s review has been written. Even more helpfully, those terms provide strong hints at the likely outcome of said review, which is likely to recommend the following:
- The publication of forecasts for the future interest rate path, rather than the current approach of basing projections on both the market rate curve, and a constant rate over the forecast horizon
- Increased use of economic scenarios, to explain the aforementioned high levels of uncertainty, and to replace the MPC’s ‘fan charts’
- A switch to the Bank’s economic forecasts being produced by Bank staff, and a move away from the current ‘best collective judgement’ of the MPC
Before digging into those in more depth, it is worth taking a step back to consider why the review is necessary in the first place.
Put simply, the post-covid inflationary surge was a particularly damaging one for the ‘Old Lady’, with woefully inaccurate forecasts, combined with a plethora of communications gaffes (Governor Bailey’s ‘don’t ask for a pay rise’ line springs to mind), caused significant damage to the Bank’s credibility, but also to public confidence in the BoE. While, in many ways, the BoE’s forecasting was no worse than that of G10 peers, there is clearly a desire within the Bank to avoid a repeat situation in the future, wrestle back control of the inflation narrative, and restore confidence in the institution.
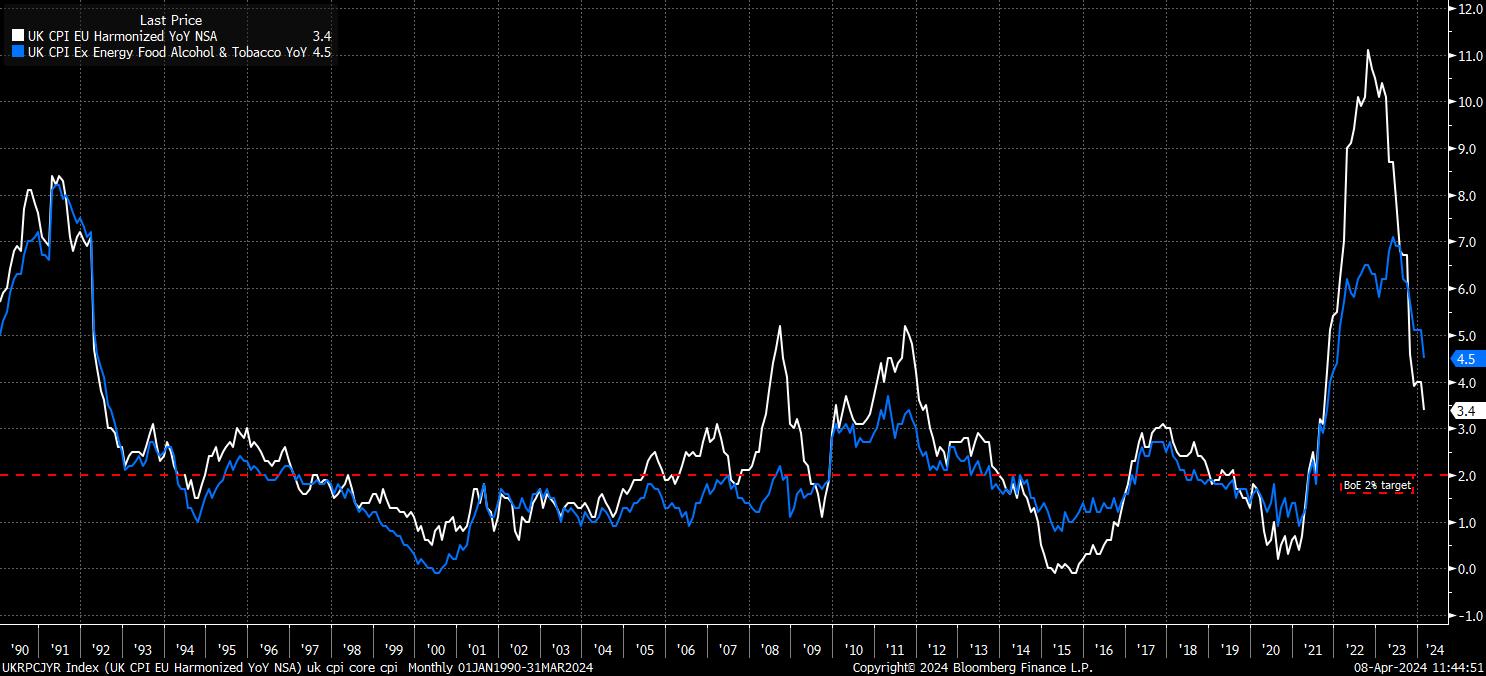
In many ways, the MPC’s current forecasting methodology left them somewhat ‘hemmed in’ during the period of double-digit inflation seen after the pandemic.
By basing economic forecasts on either a constant rate path, or the market-implied rate path, the Bank ended up consistently underestimating inflation on the way up, only to begin overestimating inflation almost as soon as CPI peaked in the fourth quarter of 2022. Clearly, this is more than simply a random forecasting error, and implies a mechanical issue at play.
Furthermore, reliance on those two distinct rate paths has resulted in two significant problems:
- The MPC’s own view on the future direction of Bank Rate is never explicitly known, instead having to be implied by strategists (including your scribe) by the difference between the inflation path under each of the paths, and which returns inflation to target the quickest
- In times of significant uncertainty, such as immediately post-Brexit, or after the Truss/Kwarteng ‘mini-budget’ of 2022, the MPC have, slightly laughably, ended up rejecting their own economic forecasts, due to volatility in rates markets upon which the projections are based
Moreover, at present it is nigh-on impossible for the MPC to communicate alternative scenarios, particularly in the event of supply shocks, of which we have seen several (Brexit, covid, supply chain backlogs, etc.) in recent times. This is primarily a result of the Committee resolutely sticking to a ‘one meeting at a time’ approach to policymaking, in addition to the use of so-called ‘fan charts’ to illustrate various potential inflation and growth paths.
To put it bluntly, those fan charts are essentially useless at achieving that, essentially conveying that policymakers have incredibly little confidence in where key economic variables are likely heading. Furthermore, the uncertainty bands associated with said charts are almost comically wide, with the February MPR including fan charts which pointed, 3 years ahead, to inflation ending up anywhere between outright deflation, or rising as high as 4%.
This, in turn, contributes to the significant communications ‘difficulties’ that the MPC have experienced this cycle. Presently, it is not possible for the MPC to communicate either its own view on the rate path, or to communicate its expectations for how the economy is most likely to develop. Nor is there any resource upon which policymakers can lean to justify policy choices, or to help answer questions such as why rates should rise, in order to tackle supply-driven inflation.
Helpfully, there is a relatively straightforward solution, or solutions, to these issues.
Namely, this would involve the MPC publishing a range of scenarios, including a ‘base case’, and a range of alternatives. These scenarios would be based upon the MPC’s preferred path of interest rates, rather than any market curve, improving the forecasts’ consistency, and allowing easier explanation of the MPC’s policy choices. Production of these scenarios would then be handed over to Bank staff, to allow the MPC to focus on considering, and subsequently publishing, how it would plan to respond if these alternatives were to pan out. This would be a relatively similar model to the one followed by Sweden’s Riksbank.
Of course, basing forecasts on the MPC’s view of the likely Bank Rate path raises the rather undesirable question of whether Bernanke recommends the Bank publish its own ‘dot plot’, akin to that issued by the FOMC, having instigated the latter back in 2012. Such a move seems relatively unlikely, owing both to the comparatively smaller size of the MPC (9 members vs. the FOMC’s 19), and as a result of apparent reluctance from a host of MPC members, including Governor Bailey, as to the utility of such a plot as a forecasting device.
This all, logically, begs the question of what – if any – market impact the Bernanke review will have.
In the short-term, any impact on the GBP, or on gilts, is likely to be relatively limited, with the review’s recommendations (which are non-binding) likely to take around 9-12 months to be fully implemented.
_2024-04-08_11-42-55.jpg)
That said, over the medium-term, the review is likely to change the relationship between markets and the Bank, albeit while continuing to recognise that any forecasts, no matter how they are produced, will naturally involve some degree of error. This relationship should shift as the BoE move away from the current ‘meeting-by-meeting’ approach, and instead attempt to take a more proactive role in shaping the economic, and policy, narratives. It will, however, take some time for both markets, and the Bank, to adapt to this new regime.
Related articles
此處提供的材料並未按照旨在促進投資研究獨立性的法律要求準備,因此被視為市場溝通之用途。雖然在傳播投資研究之前不受任何禁止交易的限製,但我們不會在將其提供給我們的客戶之前尋求利用任何優勢。
Pepperstone 並不表示此處提供的材料是準確、最新或完整的,因此不應依賴於此。該信息,無論是否來自第三方,都不應被視為推薦;或買賣要約;或征求購買或出售任何證券、金融產品或工具的要約;或參與任何特定的交易策略。它沒有考慮讀者的財務狀況或投資目標。我們建議此內容的任何讀者尋求自己的建議。未經 Pepperstone 批準,不得復製或重新分發此信息。



